IOzone is a famous file system benchmark tool in *nix world. In this post, I'll show you how to port it to Android and how to use it to benchmark both flash and Ramdisk's performance.
Build IOZone with AOSP
I work on AOSP tree on daily basis, so it's handy for me to incorporate it into
AOSP tree to take advantage of the AOSP tool chain. The key part is to come up
with a appropriate Android.mk file so that it gets built along with other
sub-projects of AOSP.
First, download IOzone source tarball from its website. I'm using the latest
tarball as of now (12/31/2014) with version 3.429. Then extract it to
external/iozone--the usual place where we put all external upstream repos.
Add a Android.mk file like this:
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
OBJS = iozone.o libbif.o
ALL = iozone
%.o: %.c
@$(NQ) ' CC ' $@
$(Q)$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c -o $@ $<
iozone: $(OBJS)
$(CC) $(LDFLAGS) $(OBJS) -lrt -lpthread -o iozone
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := $(patsubst %.o,%.c,$(OBJS))
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -Wall -DANDROID -DO_RSYNC=0 -DNO_THREADS
LOCAL_CFLAGS += -O3 -Dunix -DHAVE_ANSIC_C -DNAME='"linux-arm"' -DLINUX_ARM -Dlinux
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES := $(KERNEL_HEADERS)
LOCAL_LDFLAGS := -Wl,--no-fatal-warnings
LOCAL_MODULE_TAGS := eng
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := libc
LOCAL_LDLIBS += -lpthread
LOCAL_MODULE := iozone
include $(BUILD_EXECUTABLE)
Changes against the original Makefile that comes with the source code are:
- Do not build
fileop.c,libasync.candpit_server.c. They're not compatible with AOSP source and we will not use them anyway. - Define
ANDROIDinCFLAGS, which we'll use for some minor changes to the source code later. - Define
O_RSYNC, somehow this flag definition is missing in AOSP'sfcntl.h. - The second part of
CFLAGSis copied from the originalMakefile'slinux-armtarget. - Add user space kernel headers to include path.
- Add
libcandlibpthread.
Then we need to modify the source code a little bit to cope of AOSP's header files.
Changes for iozone.c:
diff --git a/iozone.c b/iozone.c
index 85fdea0..36de106 100644
--- a/iozone.c
+++ b/iozone.c
@@ -403,8 +403,12 @@ typedef long long off64_t;
#include <sys/time.h>
#ifdef SHARED_MEM
+#ifdef ANDROID
+#include <linux/shm.h>
+#else
#include <sys/shm.h>
#endif
+#endif
#if defined(bsd4_2) && !defined(MS_SYNC)
#define MS_SYNC 0
Changes for libbif.c:
diff --git a/libbif.c b/libbif.c
index 890e226..f997e74 100644
--- a/libbif.c
+++ b/libbif.c
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/file.h>
-#if defined(__AIX__) || defined(__FreeBSD__) || defined(__DragonFly__)
+#if defined(__AIX__) || defined(__FreeBSD__) || defined(__DragonFly__) || defined(ANDROID)
#include <fcntl.h>
#else
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
Finally, add iozone to your PRODUCT_PACKAGES so that it gets built when you
do make in AOSP root directory.
Benchmark Results
IOZone has a bunch of options. You can find the full document here. The options I used in this benchmark are:
-a: auto mode.-z: test all record size. In particular, for larger files, test with small record sizes (4K, 8K, etc.)-n 4k: specify minimum file size to test.-g 512m: specify maximum file size to test.-e: includefsyncandfflushwhen calculating time.-o: force write synchronously to disk.-p: purge cache before each file operation.-f: specify test file path. I tested with both/sdcard/test.binfor flash and/mnt/asecfor Ramdisk (or tmpfs).
The smartphone I used is Nexus 5 (hammerhead) running Android 4.4.4 KitKat. Here are the results:
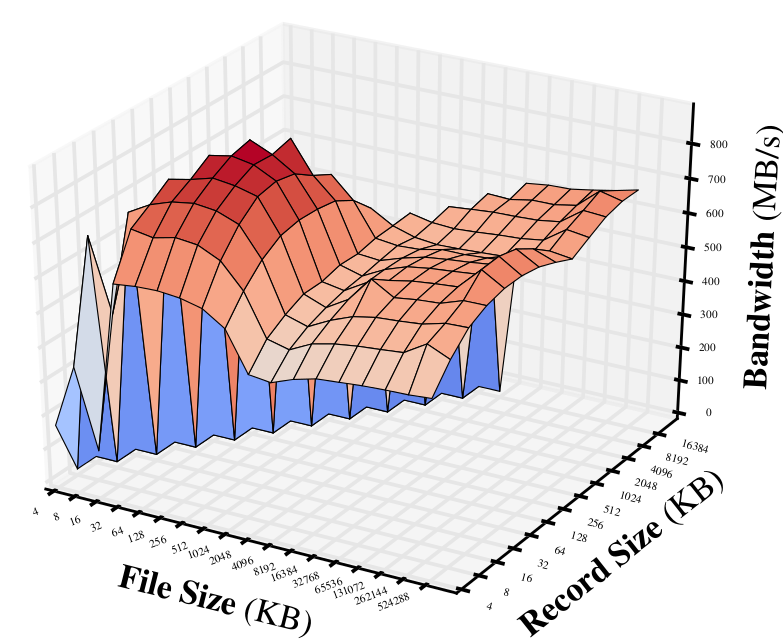
Flash Read:
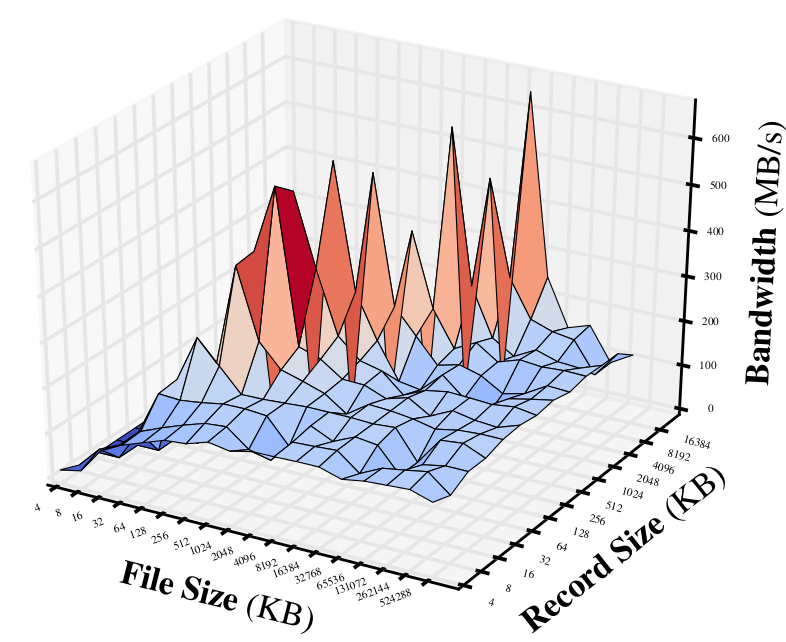
Flash Write:
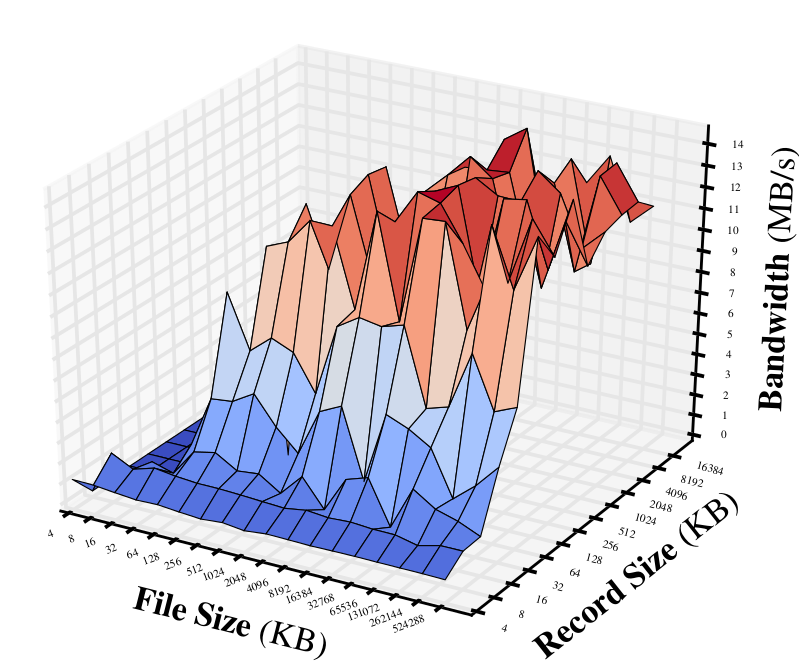
Ramdisk Read:
Ramdisk Write:
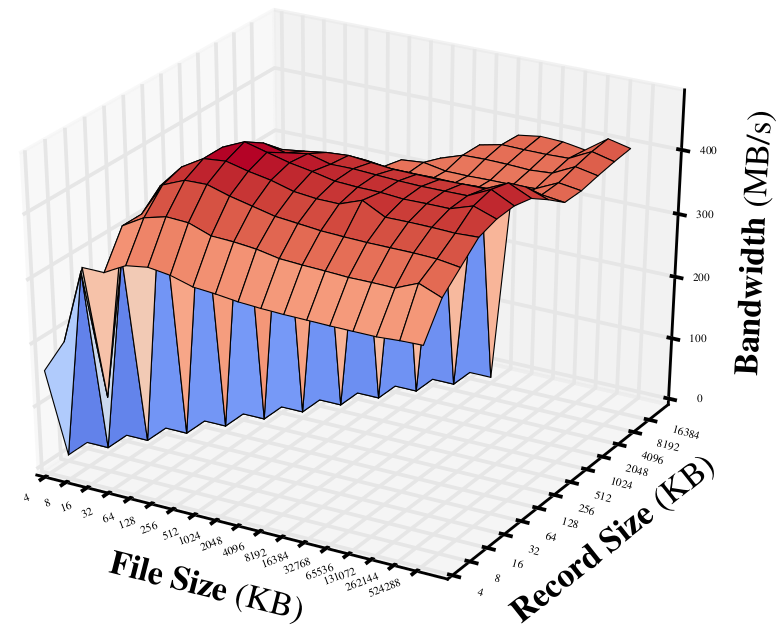
We can see that:
- The overall bandwidth with flash fluctuates a lot with different file or record size. While the bandwidths for Ramdisk are quite stable.
- As expected, the read throughput of flash is much better than write.
- The bandwidth of Ramdisk can be faster than flash in order of magnitudes.
- One particularly interesting phenomena is that, for flash read, when the record size is equal to the file size (4k-16M), the bandwidth is ridiculously high (~500MB/s). Not sure about the reason yet.